A calcium salt of malic acid, enhancing calcium solubility and gut absorption. It combines calcium with energy-supporting properties (Krebs cycle intermediate), used in bone health supplements or fortification of acidic foods.
| Calcium Malate | 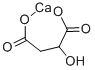 |
| CAS | 17482-42-7 |
| molecular weight | 172.15 |
| molecular formula | C4H4CaO5 |
| solubility | Methanol (slightly soluble, heated), water (slightly soluble, heated, ultrasonic treatment) |
| color | White to off-white |
| flavor | Odorless |
| state | Solid |
| melting point | >300℃ |
| boiling point | 306.4ºC |
Calcium malate, a compound formed by chelating calcium with malic acid (a naturally occurring organic acid found in fruits like apples), offers a unique blend of benefits that enhance calcium absorption, support bone health, and promote overall wellness. Here’s a breakdown of its key advantages:
1. Superior Bioavailability & Efficient Absorption
Enhanced Solubility: Malic acid forms a stable, water-soluble complex with calcium, protecting it from binding with dietary inhibitors (e.g., oxalates, phytates) in the gut. This increases calcium uptake by up to 25–30% more than calcium carbonate, ensuring more mineral reaches bones and cells, even in low-acid environments (e.g., the intestines of older adults or those taking acid-suppressing medications).
pH-Independent Absorption: Unlike calcium carbonate (which relies on strong stomach acid to dissolve), calcium malate is absorbed efficiently throughout the digestive tract—ideal for individuals with sensitive digestion, low gastric acid, or gastrointestinal conditions, such as IBS or acid reflux.
2. Gentle on the Digestive System
Reduced Risk of Constipation: Traditional calcium salts (e.g., calcium oxide, carbonate) often cause constipation due to their binding effects in the intestines. Malic acid’s organic structure minimizes this issue, promoting smoother digestion and better tolerance, even at higher doses—making it a preferred choice for long-term supplementation without digestive discomfort.
Balanced Osmotic Activity: Malic acid buffers calcium’s potential to draw water into the intestines, reducing the risk of diarrhea or cramping, ensuring consistent nutrient uptake while supporting gut health.
3. Targeted Support for Bone Health & Mineralization
Optimal Bone Mineralization: Delivers bioavailable calcium directly to osteoblasts (bone-building cells), facilitating the formation of hydroxyapatite (the mineral matrix of bones and teeth). This enhances bone density, strength, and resilience, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures—especially beneficial for postmenopausal women, older adults, and individuals with calcium deficiencies.
Energy Metabolism Synergy: Malic acid is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), which generates ATP (energy) for cellular processes. By supporting energy production in osteoblasts, calcium malate enhances calcium utilization for bone formation, ensuring efficient mineralization even during periods of high demand (e.g., growth, recovery from injury).
4. Antioxidant & Inflammatory Support
Dual Action for Cellular Health: Malic acid acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress in bone and muscle cells. This protects tissues from inflammatory damage, potentially lowering the risk of age-related bone loss and supporting overall immune health.
pH Regulation: Helps maintain a balanced pH in bodily fluids, directing calcium to skeletal tissues rather than soft tissues (e.g., arteries, kidneys), where it can cause calcification. This ensures calcium is used where it’s needed most—for bone and teeth strength.
5. Nutrient Synergy & Versatile Applications
Enhanced Iron Absorption: Malic acid improves the absorption of non-heme iron (from plant sources), making calcium malate a strategic choice for vegetarians, vegans, or individuals at risk of iron deficiency. This dual benefit addresses two common nutrient gaps in a single supplement.
Flexible Formulation: Its solubility, mild taste, and stability make it suitable for various supplement formats (tablets, capsules, powders, liquids) and fortified foods (e.g., juices, plant-based milks, snacks). It integrates seamlessly into multi-nutrient formulas, often paired with vitamin D (to enhance calcium uptake) or magnesium (for muscle and nerve support).
6. Suitable for All Life Stages
Pediatric to Geriatric Use: Gentle enough for children (supporting bone growth and development) and ideal for older adults (combating age-related absorption issues and bone loss). Its low risk of interactions with medications or other minerals also makes it safe for prenatal supplements (meeting increased calcium demands during pregnancy) and senior care.
7. Regulatory Safety & Natural Origins
GRAS-Approved and Biocompatible: Derived from natural malic acid (found in fruits), calcium malate is recognized as safe for human consumption by regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, EFSA), ensuring consumer trust and compliance for daily use.
Calcium malate stands out for its unique combination of high absorbability, digestive gentleness, and metabolic synergy, offering targeted support for bone health, energy production, and cellular protection. It’s an excellent choice for individuals seeking an effective, well-tolerated calcium supplement—particularly those with digestive sensitivities, nutrient absorption challenges, or a need for balanced mineral support in plant-based diets.
Calcium malate’s unique molecular structure—binding calcium with malic acid—creates a highly bioavailable complex that surpasses traditional calcium salts in delivering calcium to skeletal tissues:
Efficient Gut Uptake: Malic acid protects calcium from binding with dietary inhibitors (e.g., oxalates, phytates) in the intestines, increasing absorption by up to 30% compared to calcium carbonate. This ensures more calcium is available for bone mineralization—the process of depositing calcium into the bone matrix as hydroxyapatite, the mineral complex that gives bones their rigidity and strength.
pH-Independent Solubility: Unlike calcium carbonate (which relies on stomach acid to dissolve), calcium malate remains soluble across the digestive tract, making it ideal for individuals with age-related or medication-induced reductions in gastric acid. This consistency is critical for older adults, where efficient calcium delivery directly combats age-related bone density loss.
Malic acid, a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), fuels the energy demands of osteoblasts—cells responsible for constructing new bone tissue:
Osteoblast Activation: By enhancing ATP (energy) production in osteoblasts, calcium malate supports the synthesis of collagen (the protein framework of bones) and the deposition of calcium into bone matrix. This dual action strengthens bone microarchitecture, reducing vulnerability to fractures and improving overall skeletal resilience.
Antioxidant Protection for Bone Cells: Malic acid acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals that cause oxidative stress in osteocytes (mature bone cells) and osteoblasts. This protection preserves cell function and reduces inflammation, critical for maintaining the integrity of bone tissue over time—especially in postmenopausal women, where oxidative stress accelerates bone loss.
Healthy bone structure depends on a delicate balance between bone formation (by osteoblasts) and bone resorption (by osteoclasts). Calcium malate influences this process in two key ways:
Stimulates Bone Formation: By delivering bioavailable calcium and supporting osteoblast energy, it promotes the laying down of new bone tissue, essential for repairing microdamage and maintaining density.
Inhibits Excessive Resorption: Maintaining optimal calcium levels in the bloodstream via efficient absorption helps suppress overactive osteoclasts, preventing excessive breakdown of bone matrix. This balance is particularly vital in conditions like osteoporosis, where bone resorption outpaces formation, leading to fragile bones.
Clinical studies link calcium malate supplementation to reduced markers of bone turnover (e.g., tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase), indicating a more stable skeletal structure.
Calcium malate’s digestive tolerance makes it a sustainable choice for lifelong bone support:
Low Risk of Side Effects: Unlike calcium carbonate or oxide, which can cause constipation or stomach irritation, the malic acid complex minimizes osmotic pressure in the intestines, ensuring comfortable, long-term use—critical for compliance in populations at highest risk of bone loss (e.g., seniors, postmenopausal women).
Natural Synergy with Diet: Derived from malic acid (found in apples and other fruits), it aligns with consumer preferences for natural ingredients while enhancing the absorption of non-heme iron (from plant sources), making it ideal for vegans or vegetarians who may rely on plant-based diets for calcium and iron.
Why Calcium Malate Matters for Bone Structure
By merging the mineral density benefits of calcium with the metabolic and protective advantages of malic acid, calcium malate offers a multifaceted approach to bone health. It ensures calcium is not just consumed but effectively utilized to build, maintain, and repair bone tissue—addressing the root mechanisms of skeletal strength and resilience.
For anyone seeking to preserve bone structure—from growing children to older adults navigating age-related challenges—calcium malate provides a science-backed, gentle solution that supports the intricate processes required for lifelong bone health.