A family of calcium-phosphorus salts (e.g., tribasic, dibasic), critical for bone and teeth health. Used in supplements, food fortification, and as an anti-caking agent, they provide essential minerals for skeletal structure and energy metabolism
| Calcium Phosphate | 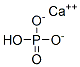 |
| CAS | 7757-93-9 |
| molecular weight | 136.06 |
| molecular formula | CaHO4P |
| solubility | Almost insoluble in water |
| color | White |
| flavor | Odorless and tasteless |
| state | Gel (aged) |
| melting point | 370°C |
| boiling point | / |
Calcium phosphate, a naturally occurring mineral compound combining calcium and phosphorus (two essential nutrients for life), offers a wide range of benefits across nutrition, medicine, industry, and agriculture. Its role in supporting bone health, enabling nutrient delivery, and enhancing product functionality makes it a cornerstone ingredient in diverse fields. Here’s a breakdown of its key advantages:
1. Core Nutritional Support for Bone & Teeth Health
Calcium phosphate is a primary component of the body’s skeletal system, providing structural and functional benefits:
Bone Mineralization & Density:
Composes ~70% of bone mass and ~85% of teeth enamel as hydroxyapatite (a calcium phosphate crystal), ensuring rigidity, strength, and resistance to fractures. Dietary calcium phosphate supplements (e.g., dicalcium phosphate, tricalcium phosphate) help maintain bone density, particularly for older adults (reducing osteoporosis risk) and growing children (supporting skeletal development).
Enhances calcium and phosphorus absorption in the intestines, working synergistically with vitamin D to regulate mineral balance and prevent deficiencies (e.g., rickets in children, osteomalacia in adults).
Dental Enamel Protection:
Reinforces tooth structure by promoting remineralization, repairing minor enamel damage (e.g., early cavities) and reducing sensitivity to hot/cold stimuli. Found in toothpaste and oral care products, it helps combat acid erosion from diet or bacteria.
2. Bioavailable Mineral Source in Supplements & Fortified Foods
As a highly absorbable form of calcium and phosphorus, it addresses nutrient gaps in modern diets:
Dietary Supplements:
Used in tablets, capsules, and powders to deliver both minerals in a single dose, ideal for vegan/vegetarian diets (low in animal-derived calcium), pregnant/lactating women (increased mineral needs), and athletes (supporting muscle contraction and energy metabolism).
Forms like calcium monophosphate and dicalcium phosphate are preferred for their solubility, ensuring efficient uptake without gastrointestinal side effects (e.g., constipation, which can occur with calcium carbonate).
Food Fortification:
Added to dairy alternatives (plant-based milks, cheeses), baked goods, cereals, and infant formulas to boost calcium and phosphorus content, aligning with global efforts to combat malnutrition and support immune function (phosphorus is critical for ATP energy production and cell membrane integrity).
3. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
Calcium phosphate’s biocompatibility and osteoconductive properties make it invaluable in healthcare:
Bone Tissue Engineering & Repair:
Used as a bone graft substitute (e.g., hydroxyapatite coatings on implants) to promote new bone growth, fill bone defects (e.g., after trauma or surgery), and enhance the integration of metal implants (e.g., hip/knee replacements) with surrounding tissue.
In dentistry, it supports socket preservation after tooth extraction and accelerates healing in periodontal surgeries.
Drug Delivery Systems:
Serves as a carrier for antibiotics, growth factors, or anti-cancer drugs in controlled-release formulations, ensuring targeted delivery to bones or teeth while minimizing systemic side effects.
Antacid and Digestive Support:
In oral medications, it neutralizes excess stomach acid to relieve heartburn and indigestion, acting as a mild, calcium-rich alternative to synthetic antacids.
4. Industrial and Functional Food Applications
In manufacturing, calcium phosphate enhances product quality and functionality:
Food Additive for Texture & Stability:
Emulsifier/Stabilizer: Maintains uniform texture in processed cheeses, sauces, and dairy products by binding water and fat, preventing separation.
pH Buffer: Regulates acidity in beverages, canned foods, and dressings, ensuring microbial safety and shelf-life while enhancing flavor balance (e.g., reducing bitterness in fortified drinks).
Anticaking Agent: Used in powders, seasonings, and supplements to prevent clumping, ensuring easy dispersion and dosage accuracy.
Industrial and Material Sciences:
Ceramics and Glass: As a raw material for heat-resistant ceramics (e.g., dental crowns, ovenware) and phosphate glass (used in medical implants).
Fertilizers: Provides phosphorus to soils in agricultural applications, supporting plant root development, photosynthesis, and crop yield (though often used as phosphate salts like triple superphosphate).
5. Safety, Sustainability, and Regulatory Compliance
Calcium phosphate’s appeal is amplified by its natural origins and global approval:
Biocompatible and Non-Toxic:
Naturally present in the human body and dietary sources (e.g., milk, nuts, legumes), it has no reported toxicity at recommended doses, making it safe for long-term use in supplements and food fortification.
GRAS-Approved and Regulated:
Recognized as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by the FDA and approved by EFSA for use in food, medicine, and cosmetics, ensuring compliance in global markets.
Eco-Friendly and Renewable:
Mined from phosphate rock or produced synthetically to mimic natural hydroxyapatite, it supports sustainable practices in healthcare (biodegradable bone grafts) and agriculture (mineral recycling in fertilizers).
6. Metabolic and Cellular Functions
Beyond bones and teeth, calcium phosphate supports whole-body physiology:
Energy Production: Phosphorus, as part of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), is essential for converting food into usable energy, critical for muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and cellular processes.
Enzyme Activation: Acts as a cofactor for hundreds of enzymes involved in carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism, ensuring efficient nutrient utilization.
Cell Membrane Integrity: Phospholipids (containing phosphorus) form the basis of cell membranes, regulating nutrient transport and protecting cellular structures.
Who Benefits from Calcium Phosphate?
Health-Conscious Individuals: Boosting bone density, supporting dental health, and filling nutrient gaps.
Medical Professionals: Using it for bone repair, drug delivery, and digestive care.
Food Manufacturers: Enhancing texture, stability, and nutritional value in products.
Athletes and Active Lifestyles: Supporting muscle function, energy metabolism, and injury recovery.
Sustainable Brands: Leveraging its natural, biocompatible properties for eco-friendly formulations.
Calcium phosphate stands out as a multifunctional nutrient and industrial ingredient, bridging the gap between essential biological roles and practical applications. From strengthening bones to stabilizing food textures, its versatility, safety, and scientific validation make it an indispensable component in products that prioritize health, functionality, and sustainability. Whether as a daily supplement, a medical implant, or a food additive, it embodies the harmony between nature’s design and human innovation.
Calcium phosphate acts as a key acidic component in baking powders and leavening systems, driving the critical reaction that creates air pockets in dough and batter:
Acid-Base Reaction with Baking Soda:
When combined with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), water-soluble forms like monocalcium phosphate (MCP) release hydrogen ions, triggering a reaction that produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas. This gas gets trapped in gluten or starch networks, causing dough to rise during mixing (initial burst) and baking (heat-activated second phase), resulting in a light, airy crumb in cakes, cookies, and quick breads.
Timed Release for Optimal Leavening:
Different calcium phosphate salts (e.g., monocalcium phosphate for fast reaction, dicalcium phosphate for slower release) allow formulators to control gas production. Fast-acting MCP provides immediate rise during mixing, while slower-release forms ensure sustained expansion in the oven, preventing collapse and ensuring uniform texture—critical for delicate pastries or dense batter like muffins.
Beyond gas production, calcium phosphate improves the physical properties of dough, enabling better handling and final product quality:
Gluten Strengthening & Elasticity:
In yeast-leavened breads and pizza doughs, calcium ions from calcium phosphate interact with gluten proteins, enhancing their cross-linking and elasticity. This strengthens the dough’s ability to trap gas, resulting in larger air cells, improved rise, and a chewier texture—especially beneficial for whole-grain or high-fiber doughs, where gluten integrity can be compromised.
pH Regulation for Enzyme Activity:
Maintains an optimal pH environment for amylase and protease enzymes in dough, promoting starch breakdown into sugars (food for yeast) and protein softening. This accelerates fermentation, enhances flavor development (via Maillard reactions), and ensures consistent rise in artisan breads or sourdoughs that rely on natural leavening.
Anti-Caking and Moisture Control:
As an anticaking agent in pre-mixed baking blends, it prevents clumping of dry ingredients (flour, sugar, leavening agents), ensuring uniform distribution and reliable leavening performance. It also stabilizes moisture in batters, reducing stickiness and improving oven spring (the final rise during baking).
Calcium phosphate adds functional and nutritional value to baked goods, aligning with modern consumer trends:
Calcium & Phosphorus Enrichment:
As a bioavailable source of two essential minerals, it boosts the nutritional profile of baked goods—ideal for fortified breads, breakfast pastries, or infant cereals. Calcium supports bone health, while phosphorus aids energy metabolism and cell repair, making it a strategic addition to “better-for-you” products.
Clean Label Compliance:
Derived from natural minerals or synthetically produced to match food-grade standards, calcium phosphate is recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA and often listed as “calcium phosphate” on ingredient labels—appealing to consumers seeking simple, recognizable additives. It replaces more complex synthetic acids (e.g., sodium aluminum phosphate) in organic, non-GMO, or premium baked goods, ensuring leavening efficacy without compromising clean-label claims.
Calcium phosphate works hand-in-hand with other baking components to solve common formulation challenges:
Sugar and Fat Reduction:
In low-calorie or low-fat baked goods, it enhances the perception of texture and moisture, compensating for the absence of fats that typically contribute to tenderness. Its leavening power ensures products remain light and fluffy even with reduced lipid content.
Gluten-Free Formulations:
In gluten-free flours (e.g., rice, almond, tapioca), it stabilizes batters by improving water retention and gas entrapment, mimicking the structural support of gluten. This is critical for achieving acceptable rise and texture in gluten-free breads, cakes, and cookies.
Why Calcium Phosphate is a Baker’s Secret Weapon
By addressing three core baking needs—leavening control, dough structure, and nutritional value—calcium phosphate offers a triple-threat solution:
Technical Precision: Ensures consistent gas production, whether for a delicate sponge cake or a hearty artisan loaf.
Texture Excellence: Strengthens dough, enhances rise, and stabilizes moisture for uniform, appealing crumb.
Health-Conscious Innovation: Adds essential minerals while meeting clean-label demands, future-proofing baked goods for evolving consumer needs.
From the airy crumb of a morning muffin to the chewy crust of a sourdough loaf, calcium phosphate ensures that every bake rises to the occasion—combining scientific precision with the art of baking to deliver products that are as nutritious as they are delicious.