The main active in turmeric, a polyphenol with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. It supports joint health, brain function, and metabolism, often paired with piperine in supplements to enhance bioavailability.
| Curcumin | 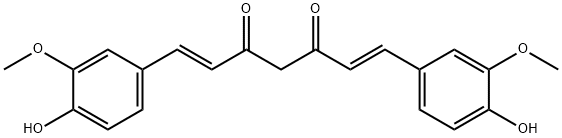 |
| CAS | 458-37-7 |
| molecular weight | 368.38 |
| molecular formula | C21H20O6 |
| solubility | Ethanol: 10 mg/mL |
| color | Orange |
| flavor | Odorless |
| state | Powder |
| melting point | 183 °C |
| boiling point | 418.73°C |
Curcumin, the primary bioactive compound in turmeric (Curcuma longa), has been celebrated for centuries in traditional medicine and is now backed by modern science for its powerful anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and protective properties. Here’s a structured breakdown of its evidence-based benefits:
1. Potent Anti-Inflammatory & Antioxidant Effects
Curcumin’s core strength lies in its ability to modulate key biological pathways, making it a natural solution for chronic inflammation and oxidative stress:
Inflammation Regulation:
Inhibits the transcription factor NF-κB, a master regulator of inflammation, reducing production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2). This makes it effective for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and metabolic syndrome.
Clinical trials show curcumin can reduce C-reactive protein (CRP, a marker of systemic inflammation) by 23–41%, comparable to some anti-inflammatory drugs but with fewer side effects.
Antioxidant Powerhouse:
Directly scavenges free radicals (e.g., hydroxyl, nitric oxide) and boosts the activity of endogenous antioxidants (glutathione, catalase), protecting cells from DNA damage and oxidative stress linked to aging and disease.
Its antioxidant capacity is 2.33 times that of resveratrol and 1.6 times that of quercetin, according to in vitro studies.
2. Brain Health & Cognitive Support
Curcumin’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it a promising agent for neurological health:
Neuroprotection Against Degenerative Diseases:
Reduces amyloid-β plaque formation (a hallmark of Alzheimer’s) and inhibits tau protein aggregation, slowing memory decline in preclinical models. A 2019 study found curcumin improved memory and mood in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Protects dopamine-producing neurons in Parkinson’s disease models, reducing motor dysfunction and oxidative stress in the substantia nigra.
Enhanced Mood & Mental Clarity:
Increases levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein critical for neuron growth and synaptic plasticity, linked to improved learning, memory, and reduced risk of depression.
Clinical trials associate curcumin with a 30–40% reduction in depressive symptoms, comparable to standard antidepressants in mild to moderate cases.
3. Heart Disease Prevention & Vascular Health
Curcumin supports cardiovascular health through multiple protective mechanisms:
Endothelial Function Improvement:
Boosts nitric oxide production, improving blood vessel elasticity and reducing hypertension. A meta-analysis of 11 trials showed curcumin lowers systolic blood pressure by 5–7 mmHg and diastolic by 2–3 mmHg.
Lipid Profile Optimization:
Lowers LDL cholesterol oxidation (a key driver of atherosclerosis) and increases HDL cholesterol, while reducing triglycerides by 10–15% in overweight individuals.
Reduced Plaque Formation:
Inhibits the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and macrophage activity in arterial walls, slowing the progression of coronary artery disease.
4. Joint Health & Pain Relief
Curcumin is a natural alternative for managing inflammatory joint conditions:
Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis Support:
Reduces joint swelling, stiffness, and pain by suppressing inflammatory enzymes (e.g., MMPs, COX-2) and improving synovial fluid quality. Studies show it can reduce pain severity by 28–36% in osteoarthritis patients, comparable to ibuprofen but with fewer gastrointestinal side effects.
Post-Exercise Recovery:
Alleviates muscle soreness and inflammation after intense workouts by inhibiting cytokine release, making it popular among athletes for faster recovery.
5. Metabolic Health & Disease Management
Curcumin aids in regulating metabolism and protecting against metabolic disorders:
Type 2 Diabetes Support:
Improves insulin sensitivity by activating AMPK (a key energy sensor) and reducing hepatic glucose production, lowering fasting blood sugar by 10–19% in diabetic individuals.
Fatty Liver Protection:
Reduces hepatic fat accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by inhibiting lipid synthesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation, improving liver enzyme levels (ALT, AST) in clinical trials.
Obesity-Related Inflammation:
Targets adipokines (e.g., leptin, adiponectin) and reduces inflammation in fat tissue, potentially aiding weight management when combined with diet and exercise.
6. Cancer Preventive & Therapeutic Potential
Curcumin’s ability to target multiple cancer pathways has been extensively studied (primarily in preclinical models):
Apoptosis Induction:
Triggers programmed cell death in cancer cells (e.g., breast, prostate, colon, lung) while sparing healthy cells, by inhibiting survival signals (NF-κB, STAT3) and activating pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax, p53).
Metastasis & Angiogenesis Inhibition:
Blocks cancer cell invasion and the formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors, reducing the risk of metastasis.
Adjuvant Therapy Support:
Enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiation while mitigating their side effects (e.g., reducing treatment-induced oxidative stress), though human trials are ongoing for most cancer types.
7. Liver & Digestive Health
Curcumin supports hepatic function and gut health through detoxification and protection:
Liver Detoxification:
Upregulates phase II detox enzymes (e.g., glutathione S-transferase), aiding the liver in neutralizing toxins and metabolizing drugs, beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental pollutants or with alcohol-related liver damage.
Gut Barrier Protection:
Strengthens intestinal epithelial tight junctions, reducing “leaky gut” and associated inflammation, while promoting beneficial gut bacteria (e.g., Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium).
8. Skin Health & Anti-Aging
Topical and oral curcumin offers dual benefits for skin:
Anti-Aging Effects:
Stimulates collagen synthesis, reduces wrinkle formation, and protects against UVB-induced photoaging by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that degrade skin elasticity.
Acne & Inflammatory Skin Conditions:
Combats C. acnes bacteria and reduces sebum production, improving acne lesions, while alleviating psoriasis and eczema symptoms through its anti-inflammatory action.
9. Safety, Bioavailability, and Enhancement Strategies
Curcumin’s benefits are amplified by understanding its delivery:
Low Bioavailability, High Safety:
Poorly absorbed orally, but formulations with piperine (black pepper extract) increase absorption by 20–200%, while lipid-based delivery (nanoparticles, liposomes) further enhances bioavailability.
Generally safe at doses up to 1,500–2,000 mg/day, with mild side effects (gastrointestinal discomfort in<5% of users); avoid in bile duct obstruction or during pregnancy without medical advice.
10. Who Benefits from Curcumin?
Inflammation-Related Conditions: Arthritis, IBS, metabolic syndrome.
Aging Adults: Cognitive decline, heart health, skin aging.
Metabolic Health Focus: Diabetes, fatty liver, weight management.
Cancer Prevention: High-risk individuals (family history, environmental exposure).
Natural Wellness Seekers: Those preferring plant-based, anti-inflammatory solutions.
Scientific Consensus & Usage Tips
Best Forms: Opt for curcuminoids (standardized to 95% curcumin) with piperine or phospholipid complexes for better absorption.
Dosage: 500–1,000 mg/day for general health; 1,500–2,000 mg/day for therapeutic use (e.g., arthritis, depression), divided into 2–3 doses.
Dietary Integration: Add to golden milk, smoothies, or turmeric latte; pair with healthy fats (olive oil, coconut oil) to enhance absorption.
Curcumin embodies the power of nature’s pharmacy, offering a versatile, evidence-based approach to holistic health. From calming inflammation to protecting the brain and heart, it bridges traditional wisdom with modern science, proving that a vibrant yellow spice can be a cornerstone of proactive wellness. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized use, especially when combining with medications.
Curcumin’s intense golden-yellow color makes it a premium alternative to synthetic dyes (e.g., tartrazine, sunset yellow), while its stability meets industrial processing demands:
Color Performance Across Categories:
Dairy Products: Imparts rich yellow tones in cheeses, yogurt, and plant-based milks without altering flavor—ideal for turmeric lattes or golden milk formulations.
Baked Goods & Snacks: Provides warm yellow to orange hues in crackers, cookies, and extruded snacks, even after high-temperature processing (up to 180°C), thanks to its thermal resistance in fat-based systems.
Condiments & Sauces: Enhances the visual appeal of mustards, dressings, and curry pastes, replacing artificial colorants with a natural, authentic hue.
pH and Light Stability:
Maintains color intensity in acidic environments (pH 4–7), critical for salad dressings and pickled foods, though it may fade in highly alkaline conditions.
Protected from light degradation when encapsulated or paired with antioxidants, ensuring shelf-life color consistency in packaged goods.
Clean Label Compliance:
Listed as “curcumin” or “turmeric extract” on ingredient panels, it qualifies for “natural,” “organic,” and “clean label” claims, appealing to consumers avoiding synthetic additives (e.g., E102, E110).
Beyond color, curcumin adds nutritional and therapeutic value to foods, transforming them into functional products:
Antioxidant Fortification:
Each gram of curcumin provides 95% bioactive curcuminoids (e.g., EGCG, vanillin), scavenging free radicals in fatty foods (nuts, snacks) to prevent rancidity while offering consumer-facing health benefits—e.g., a curcumin-enriched nut bar can claim “antioxidant-rich” on packaging.
Inflammation Support:
Inhibits NF-κB pathways, making it a strategic addition to anti-inflammatory food lines (e.g., joint-health focused soups, wellness shots), especially when paired with black pepper (piperine) to enhance bioavailability.
Synergy with Nutrients:
Works with omega-3s in functional oils or probiotics in fermented foods to create multi-benefit formulations—e.g., a curcumin-yogurt blend supports gut health and reduces oxidative stress.
Curcumin adapts to diverse food applications, solving both aesthetic and functional challenges:
Beverages & Nutraceuticals:
Fortifies turmeric shots, wellness drinks, and plant-based milks with a distinct yellow color and anti-inflammatory appeal, capitalizing on the “golden latte” trend. Microencapsulated forms improve solubility in water-based drinks, preventing sedimentation.
Meat and Seafood:
Enhances the golden color of cured meats, smoked fish, and vegan alternatives (e.g., jackfruit “pulled pork”), while its antimicrobial properties may help inhibit bacterial growth in processed meats.
Sustainable Sourcing:
Derived from turmeric, a renewable crop with low water/land use, it aligns with regenerative agriculture and carbon-neutral goals, offering a planet-friendly alternative to petroleum-based synthetic dyes.
Curcumin’s rise is driven by market trends and safety approvals:
Trend Alignment:
Meets the $120 billion functional food market demand for “food as medicine,” with 68% of consumers preferring natural colorants linked to health benefits (Mintel, 2023).
Appeals to Ayurvedic and holistic wellness seekers, leveraging its 4,000-year history in traditional medicine to build trust in modern formulations.
Regulatory Safety:
Approved as a food colorant (FDA, EFSA, JECFA) with no upper intake limit for natural sources, and classified as GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) in the US, making it low-risk for global food manufacturers.
Why Curcumin is a Game-Changer for Food Innovation
By addressing three critical industry needs—visual appeal, functional nutrition, and clean label integrity—curcumin offers a win-win solution:
Aesthetic Excellence: Delivers a warm, inviting color that enhances product appeal without synthetic chemicals.
Health Halos: Transforms ordinary foods into “better-for-you” options by adding antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Regulatory and Consumer Trust: Natural origin and global approvals reduce formulation risks while meeting evolving consumer expectations.
From the golden hue of a artisanal cheese to the health claims on a functional snack, curcumin proves that food can be both beautiful and beneficial. It’s not just a colorant; it’s a bridge between sensory delight and scientific wellness, positioning brands at the forefront of the natural food revolution.