A water-soluble polysaccharide from brown algae, acting as a thickener, emulsifier, or gelling agent in foods (sauces, desserts) and pharmaceuticals (wound dressings). It also serves as a dietary fiber for gut health and probiotic encapsulation.
| Sodium Alginate | 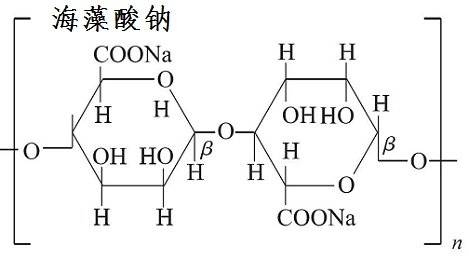 |
| CAS | 9005-38-3 |
| molecular weight | 438.7 |
| molecular formula | (C6H7O6Na)n |
| solubility | Slowly dissolves in water to form a viscous colloidal solution, almost insoluble in ethanol |
| color | White |
| flavor | Odorless |
| state | Powder |
| melting point | 99℃ |
| boiling point | 495.2℃ |
Sodium alginate, a natural polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed (such as Laminaria and Macrocystis), offers a wide range of benefits across food, health, industry, and environmental applications. Its unique gel-forming, emulsifying, and biocompatible properties make it a versatile ingredient. Here’s a breakdown of its key advantages:
1. Food Industry Applications: Texture, Nutrition, and Functionality
Premium Thickening & Stabilizing Agent:
Forms stable gels, emulsions, and foams in foods like ice cream, salad dressings, and sauces, improving texture and preventing ingredient separation.
Used in low-fat or low-sugar formulations to mimic the mouthfeel of fatty foods, reducing calorie content without compromising taste.
Dietary Fiber for Digestive Health:
As a soluble fiber, it promotes gut motility, supports probiotic growth, and aids in satiety—making it ideal for weight management products (e.g., meal replacement shakes, high-fiber snacks).
May help regulate blood sugar and cholesterol by slowing carbohydrate and lipid absorption.
Food Structuring & Encapsulation:
Creates 仿生食品 (e.g., plant-based “caviar,” vegan cheese alternatives) through calcium-induced gelation, mimicking natural textures.
Encapsulates flavors, vitamins, or probiotics to protect them from degradation during processing or storage (e.g., in fortified beverages or infant formulas).
2. Medical and Pharmaceutical Benefits: Biocompatibility and Therapeutic Support
Wound Healing Accelerator:
Forms a breathable, moisture-retaining hydrogel when applied to wounds, creating an optimal environment for tissue repair.
Absorbs exudate (wound fluid) and releases calcium ions to stimulate cell proliferation, making it effective for chronic wounds (e.g., diabetic ulcers, burns) and post-surgical incisions.
Drug Delivery System:
Serves as a carrier for oral medications, protecting acid-sensitive drugs (e.g., probiotics, enzymes) from stomach acid and enabling targeted release in the intestines.
Used in hydrogel-based implants for localized drug delivery (e.g., cancer therapies) or tissue engineering, where its biodegradability minimizes immune reactions.
Heavy Metal Detoxification:
In medical settings, oral sodium alginate binds to heavy metals (e.g., lead, cadmium) in the gut, facilitating their excretion and reducing toxicity—valuable for environmental poisoning cases.
3. Industrial and Technical Applications: Versatile Functional Properties
Textile and Printing Industry:
Acts as a thickening agent in textile dyeing and screen printing, ensuring precise color placement and reducing dye waste.
Biodegradable and eco-friendly, replacing synthetic polymers in sustainable fabric production.
Cosmetics and Personal Care:
Enhances the texture of creams, lotions, and shampoos as a gentle thickener and emulsifier, suitable for sensitive skin.
Forms a protective film on the skin, locking in moisture and delivering active ingredients (e.g., hyaluronic acid, vitamins) in face masks and anti-aging products.
Water Treatment and Environmental Remediation:
Removes heavy metals (e.g., mercury, copper) from industrial wastewater by binding to metal ions, serving as an eco-friendly flocculant.
Absorbs oils and hydrocarbons in marine spills, aiding in environmental cleanup efforts.
4. Environmental Sustainability: Renewable and Biodegradable
Natural, Plant-Based Sourcing:
Derived from fast-growing seaweed, a renewable resource that requires no freshwater, arable land, or pesticides—aligning with circular economy goals.
Biodegradable and Non-Toxic:
Breaks down naturally in soil and water, making it a safe alternative to synthetic polymers in packaging, agriculture, and industrial applications.
Agricultural Applications:
Used as a soil conditioner to retain water and nutrients, improving crop yield and reducing irrigation needs.
Encapsulates plant growth hormones or pesticides for slow-release, minimizing chemical runoff and environmental impact.
5. Safety and Regulatory Compliance
GRAS-Approved and Hypoallergenic:
Recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA and EFSA for food and medical use, with minimal risk of allergic reactions—ideal for sensitive populations.
Versatile Formulation:
Soluble in water, pH-stable, and compatible with most salts and organic compounds, enabling easy integration into diverse products without compromising efficacy.
Who Benefits from Sodium Alginate?
Food Manufacturers: Seeking clean-label, functional additives for texture, nutrition, and sustainability.
Healthcare Providers: Utilizing its wound-healing and drug-delivery properties in clinical settings.
Eco-Conscious Brands: Leveraging its biodegradability for sustainable packaging, cosmetics, and industrial solutions.
Consumers: Benefiting from its digestive health support in functional foods and gentle, natural ingredients in personal care.
Sodium alginate’s unique blend of natural origin, functional versatility, and biocompatibility makes it a standout ingredient across industries. From enhancing food texture and promoting gut health to enabling sustainable manufacturing and advanced medical therapies, it exemplifies how marine resources can drive innovation while prioritizing safety and environmental responsibility.
Sodium alginate’s defining property is its ability to form stable, reversible gels when exposed to calcium ions—a process critical for shaping and stabilizing food textures:
Controlled Gelation for Structured Foods: In applications like plant-based “caviar,” vegan cheese, or fruit snacks, calcium-induced gelation creates uniform, spherical beads or solid matrices that mimic natural textures. This precision allows manufacturers to create products(e.g., seafood substitutes, molded desserts) with realistic mouthfeel and visual appeal.
Thermal Stability for Processed Foods: Unlike many hydrocolloids, alginate gels maintain their structure under heat (e.g., in canned soups or frozen meals), preventing collapse during cooking or thawing. This stability is vital for ready-to-eat products, ensuring consistent texture from production to consumption.
Low-Calorie Texturization: By forming gels with minimal solids, sodium alginate enables low-fat or low-sugar formulations (e.g., reduced-fat ice cream, sugar-free jams) to retain a rich, creamy texture without relying on high-fat ingredients.
Sodium alginate acts as a powerful emulsifier and suspending agent, addressing the common challenge of ingredient separation in liquid or semi-liquid foods:
Stabilizing Oil-Water Mixtures: In salad dressings, sauces, and dairy alternatives, it coats oil droplets or particulates, preventing them from clumping or rising to the surface. This extends shelf-life and ensures a smooth, uniform texture in products like mayonnaise, almond milk, or creamy soups.
Controlling Viscosity with Shear Thinning: As a “pseudoplastic” fluid, sodium alginate solutions thicken at rest but flow easily when agitated (e.g., when pouring a sauce). This property enhances pumpability during manufacturing while ensuring a luxurious, clingy texture on the plate—ideal for gravies, salad dressings, or nut butters.
Suspending Insoluble Particles: In fiber-fortified beverages, grain-based drinks, or fruit juices with pulp, it keeps particles evenly distributed, eliminating sedimentation and improving sensory appeal.
One of sodium alginate’s most innovative roles is reducing calorie density while preserving mouthfeel:
Fat Replacement in Dairy and Meat Alternatives: In low-fat ice cream or yogurt, it replaces triglycerides by forming a network that traps water and air, creating a smooth, creamy texture with fewer calories. Similarly, in plant-based meats, it binds fibers and moisture, mimicking the juiciness and tenderness of animal proteins.
Sugar Substitution in Confectionery: In gummy candies or jellies, alginate gels provide chewy, elastic textures without relying on high sucrose levels. This supports the growing demand for “cleaner” snacks with reduced added sugars.
Enhancing Crust and Crunch: In battered or breaded foods (e.g., tempura, chicken nuggets), sodium alginate improves coating adhesion, forming a crispy, uniform crust that stays crunchy longer by reducing oil absorption during frying.
Beyond texture, sodium alginate safeguards sensitive components, indirectly enhancing stability and shelf-life:
Encapsulating Flavors and Nutrients: In fortified foods or functional beverages, it forms protective microcapsules around heat-sensitive vitamins (e.g., vitamin C), probiotics, or volatile flavors, preventing degradation during processing or storage. This ensures nutrients remain intact and flavors stay vibrant until consumption.
Sustaining Texture in Frozen Products: In frozen desserts or meals, alginate’s ability to retain water reduces ice crystal formation, preserving a smooth texture after repeated freezing and thawing—critical for products like ice cream sandwiches or frozen soups.
Why Sodium Alginate is a Food Formulator’s Essential Tool
By leveraging its gel-forming, emulsifying, and stabilizing powers, sodium alginate solves two core challenges in food production:
Texture Precision: It creates everything from delicate gels in artisanal desserts to sturdy structures in plant-based meats, offering endless creative possibilities.
Stability Assurance: It prevents separation, extends shelf-life, and protects sensitive ingredients, ensuring products look, feel, and taste consistent from first to last bite.
Best of all, its natural origin, clean-label appeal, and regulatory safety (GRAS-approved) make it a sustainable choice for modern food industries aiming to deliver innovation without compromising on quality or consumer trust. Whether in gourmet cuisine, everyday snacks, or functional nutrition, sodium alginate proves that nature’s polymers can transform food texture while upholding the highest standards of stability and sustainability.